
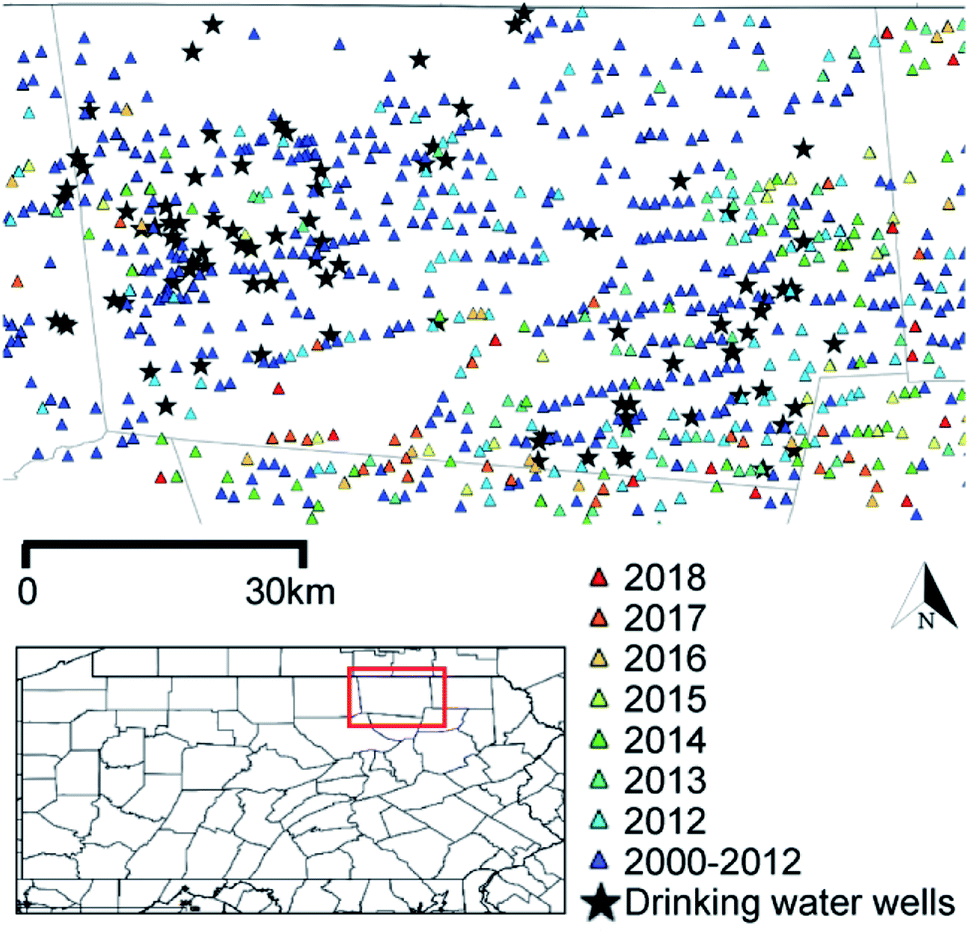
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Groundwaters in Northeastern Pennsylvania near intense hydraulic fracturing activities exhibit few organic chemical impacts
In this comprehensive study, researchers investigated the potential impact of hydraulic fracturing activities on groundwater quality in Northeastern Pennsylvania, using a HydroGeoSphere model of a region with thirty gas-well pads. Modelling results suggest a low probability of systematic groundwater organic contamination in the region.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Understanding the vulnerability of surface–groundwater interactions to climate change: insights from a Bavarian Forest headwater catchment
This study used HydroGeoSphere to evaluate the impact of climate change on streamflow and water availability within a small forested catchment in South-East Germany. Climate forecasts in the region predict a significant decrease in precipitation over the coming decades. Based on integrated hydrologic modelling of the catchment, this forecasted decline in precipitation combined with a relatively steady rate of evapotranspiration (compared to the historical period) will result in prolonged drought conditions, which in turn will result in declining groundwater levels, decreased baseflow to the upstream reaches of the stream network.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Potential influence of climate change on ecosystems within the Boreal Plains of Alberta
This paper by researchers at the University of Alberta discusses the possible impacts of climate change in the Boreal Plains in Northern Alberta, Canada. The sensitive ecosystems in this area have developed under a delicate water balance, while climate change and warming temperatures threaten to shift water availability. This study looks at ponds, peatlands with sparse black spruce, and hillslopes with predominantly aspen forests as the features of focus.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Impacts of Climate Change and Different Crop Rotation Scenarios on Groundwater Nitrate Concentrations in a Sandy Aquifer
This study by researchers at the University of Guelph investigated the impacts of various crop rotation scenarios and climate change on groundwater nitrate concentrations in a 155 sq-km agricultural sub-watershed in Norfolk County, Ontario.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Evaluating Climate Change Impacts on Soil Moisture and Groundwater Resources Within a Lake-Affected Region
This study investigates how climate change could impact groundwater and soil moisture within the Great Lakes Basin (GLB). Groundwater is a resource that is relied on for agriculture, industry, municipalities, and drinking water. Approximately one-quarter of the 33 million inhabitants of the GLB depend on groundwater as their primary freshwater source. Given its extreme value as a natural resource, the impacts of climate change on groundwater need to be well understood, and fully-integrated models that incorporate such large water bodies (let alone an entire basin-scale system) are rare.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Evaluating backward probability model under various hydrogeologic and hydrologic conditions
A new paper uses HydroGeoSphere to evaluate the reliability of a backward-in-time solute transport probability model. HydroGeoSphere was instrumental in the research as it is one of the only modelling platforms that supports 3-dimensional solute transport under variably saturated groundwater flow conditions.
