
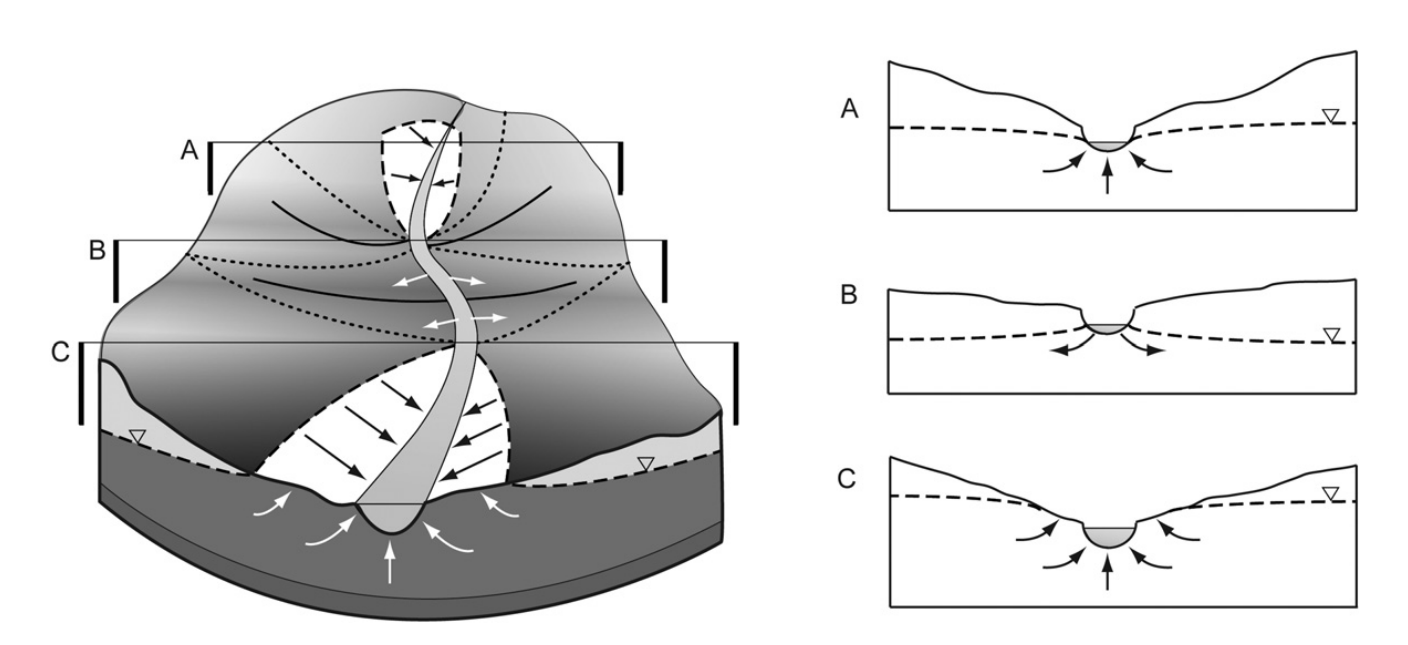
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – A hydraulic mixing-cell method to quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within spatially distributed fully integrated surface water–groundwater flow models
This research highlight co-authored by D. Partington, P. Brunner, C.T. Simmons, René Therrien, A.D. Werner, G.C. Dandy, and H.R. Maier, introduces a hydraulic mixing-cell (HMC) method to accurately quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within fully integrated surface–subsurface hydrologic models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to address long-standing challenges in decomposing streamflow generation mechanisms without relying on tracer transport simulations or simplifying assumptions about groundwater discharge.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Natural and anthropogenic drivers of the water table dynamics in a riparian fen peatland
This publication, co-authored by Adrien Renaud, Claude Mügler, Véronique Durand, and Marc Pessel, which examines the natural and anthropogenic drivers of water table dynamics in a riparian fen peatland along the Essonne River in France. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to couple surface and subsurface hydrology, providing new insights into how precipitation seasonality, vegetation activity, and river regulation influence peatland water levels.
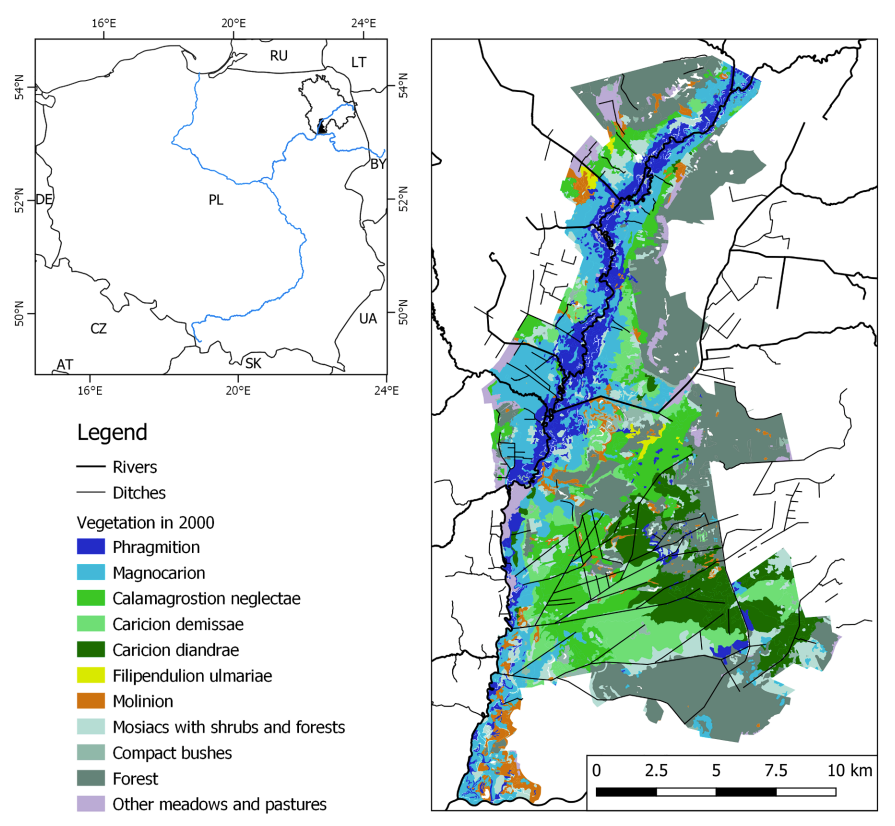
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Using water sources extent during inundation as a reliable predictor for vegetation zonation in a natural wetland floodplain
We’re pleased to highlight this publication, co-authored by Tomasz Berezowski and Martin Wassen, which investigates how the extent of water sources during inundation can be used as reliable predictors of vegetation zonation in wetland floodplains. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) together with the Hydraulic Mixing-Cell (HMC) method to address long-standing challenges in modelling vegetation dynamics by explicitly accounting for the spatial distribution of different water sources during floods.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – External and internal drivers behind the formation, vegetation succession, and carbon balance of a subarctic fen margin
In this research publication, researchers investigated the formation, vegetation succession, and carbon balance of peatland margins in Finnish Lapland. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) alongside paleoecological records and remote sensing to address long-standing challenges in understanding how new peatland areas initiate, expand, and influence climate through carbon cycling.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Model simplification to simulate groundwater recharge from a perched gravel-bed river
This publication co-authored by Antoine Di Ciacca, Scott Wilson, Patrick Durney, Guglielmo Stecca, and Thomas Wöhling, investigates model simplification strategies to simulate groundwater recharge from perched gravel-bed rivers. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) as a fully integrated 3D surface–subsurface model, alongside 2D cross-sectional and 1D analytical models, to address long-standing challenges in representing river–aquifer interactions while reducing computational demands.

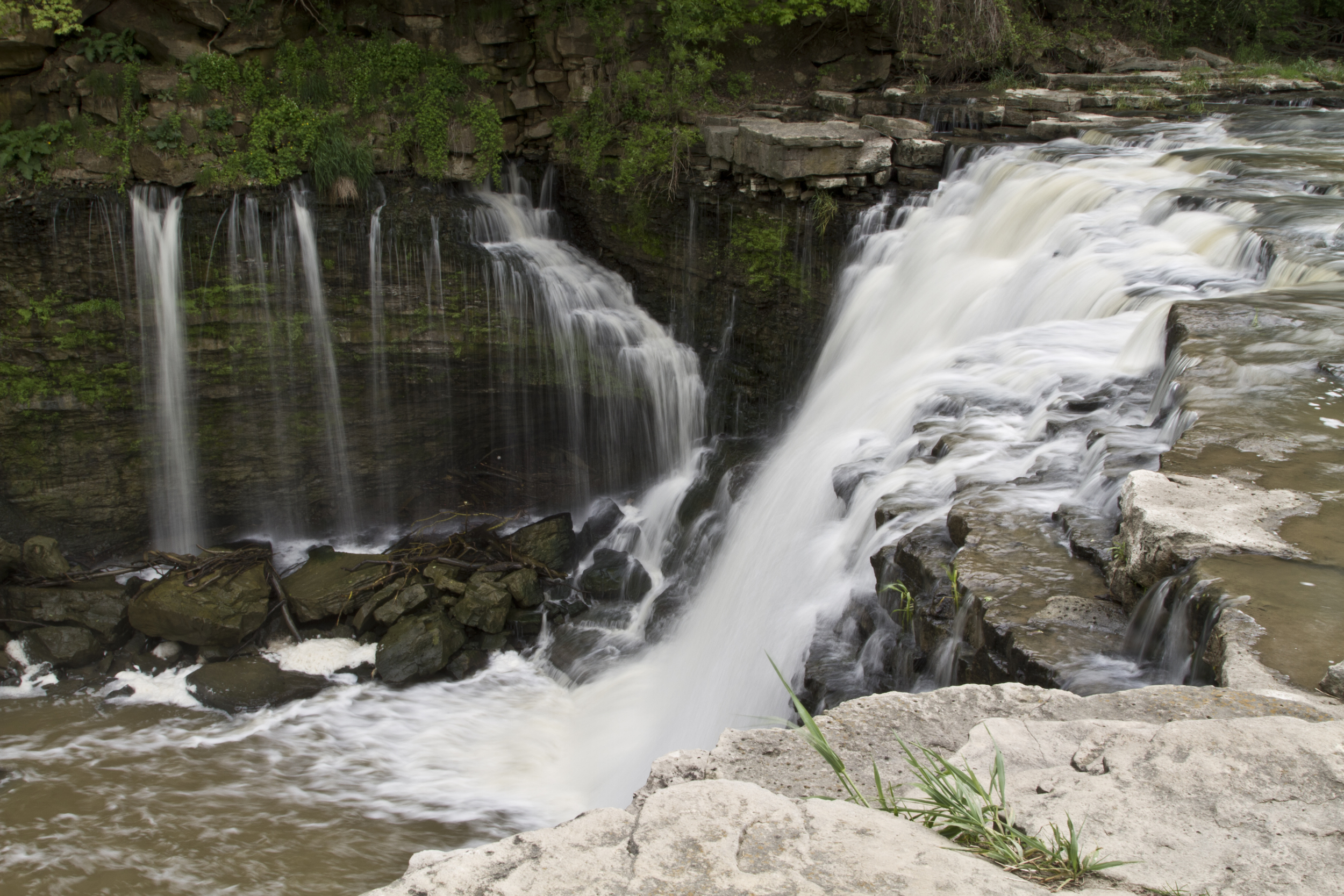
Staff Research Highlight - Understanding topography-driven groundwater flow using fully-coupled surface-water and groundwater modeling
This research focuses on understanding the dynamics of topography-driven groundwater flow systems using fully-coupled surface–subsurface hydrologic modelling. This study addresses long-standing challenges in representing nested flow systems by simulating interactions between climate, topography, and groundwater without relying on potentially unrealistic, static boundary conditions.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Vulnerability of the Saint-Charles drinking water source: portrait of the groundwater resources of the St-Charles River watershed and their links with surface water
We’re pleased to highlight this research effort, which focuses on understanding the vulnerability of the Saint-Charles River drinking water source and characterizing the groundwater resources that support it. Presented through a public-facing ArcGIS Story Map, this project delivers an accessible summary of a detailed hydrogeological study that integrates field measurements, geochemical analyses, and numerical modelling to evaluate the watershed’s current and future ability to provide safe, reliable drinking water for the City of Quebec and its surrounding municipalities.
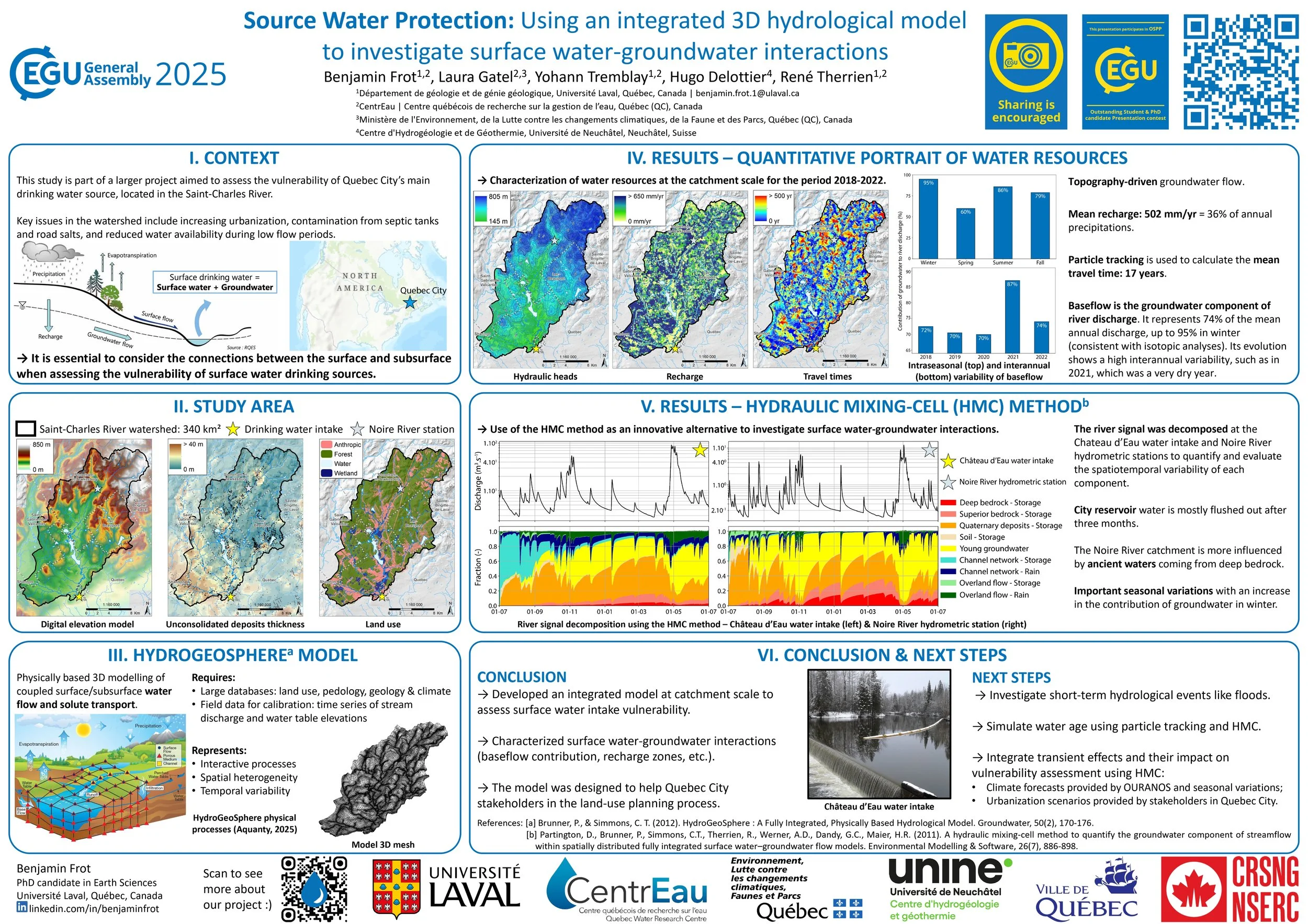
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Source Water Protection in Quebec City: Using an integrated 3D hydrological model to investigate surface water-groundwater interactions
The research, presented as a poster by Benjamin Frot at EGU 2025, explores the use of HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to investigate surface water–groundwater interactions in the Saint-Charles River watershed, which supplies drinking water to Quebec City. With a focus on source water protection, the study addresses the challenges posed by increasing urbanization, contamination from septic systems and road salts, and reduced water availability during low-flow periods. The work is part of a larger project aimed at evaluating the vulnerability of Quebec City's main surface water intake.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Exploring the reliability of ²²²Rn as a tracer of groundwater age in alluvial aquifers: Insights from the explicit simulation of variable ²²²Rn production
We’re pleased to highlight this publication which investigates the reliability of using radon-222 (²²²Rn) as a tracer for groundwater age in alluvial aquifers. Accurate estimations of groundwater residence time (GRT)—the time since water infiltrated from the surface—are critical for effective water resource management, especially in systems that rely on bank filtration near rivers for drinking water supply. While ²²²Rn has long been employed as a natural tracer due to its radioactive decay properties and elevated concentrations in groundwater, most traditional models assume spatially uniform ²²²Rn production and purely advective flow— assumptions that rarely hold in real-world aquifers.

Staff Research Highlight - A Continuous Differentiable Formulation for Seepage Face Boundary Conditions in Dynamic Groundwater Systems
This research by Aquanty staff introduces a continuously differentiable formulation for seepage face boundary conditions in dynamic groundwater systems. Traditional approaches often model seepage faces with abrupt boundary transitions, leading to numerical instabilities, convergence issues, and computational inefficiencies in transient groundwater simulations. This research presents a novel approach that ensures smooth transitions between saturated and unsaturated zones, improving the stability and accuracy of numerical groundwater models.
