
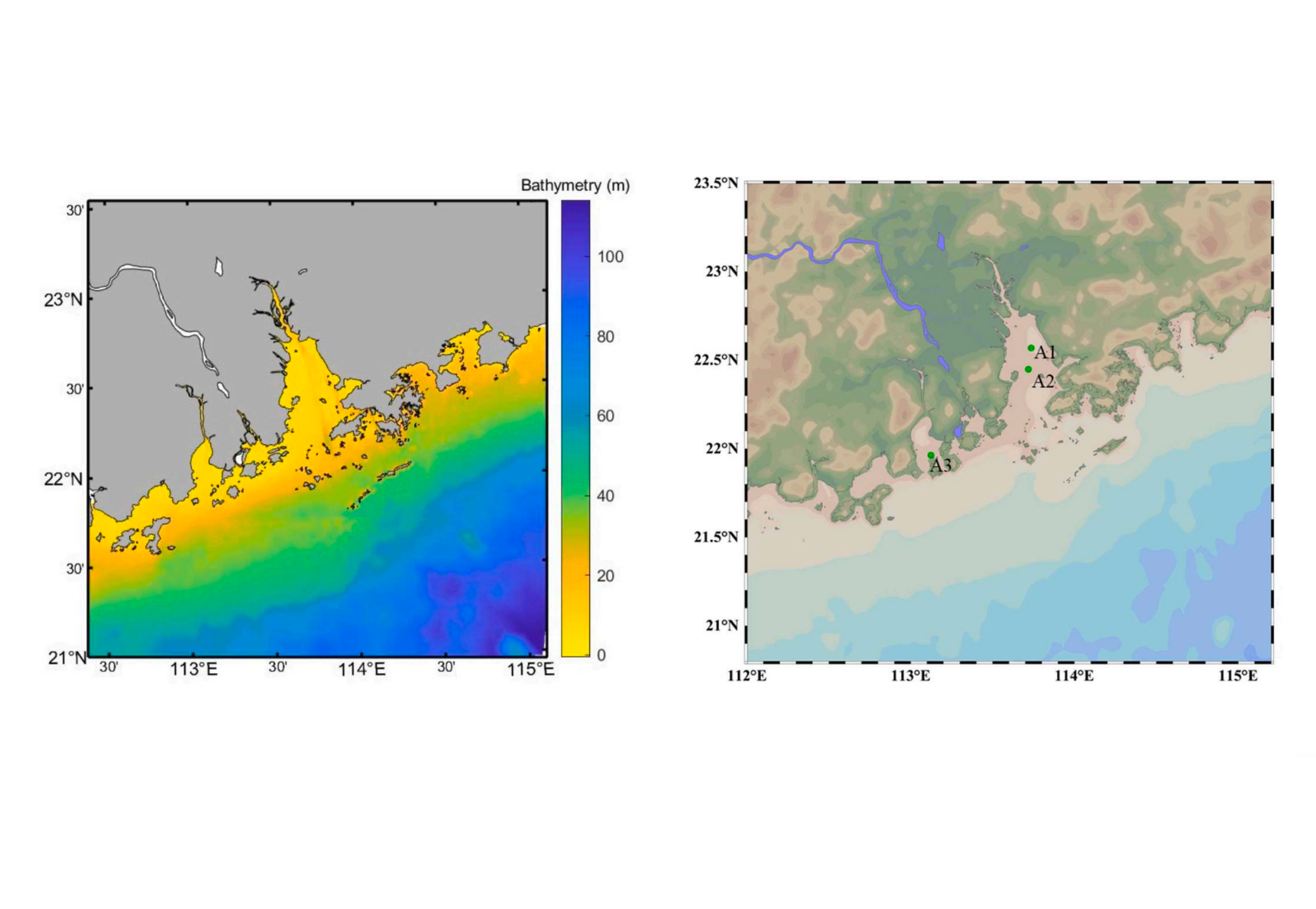
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Modeling the water use associated with energy consumption changes on saltwater intrusion in the Pearl River estuary, China
This research investigates how increased energy consumption and associated changes in water use impact saltwater intrusion in the Pearl River Estuary— one of China's most economically vital and environmentally vulnerable regions.
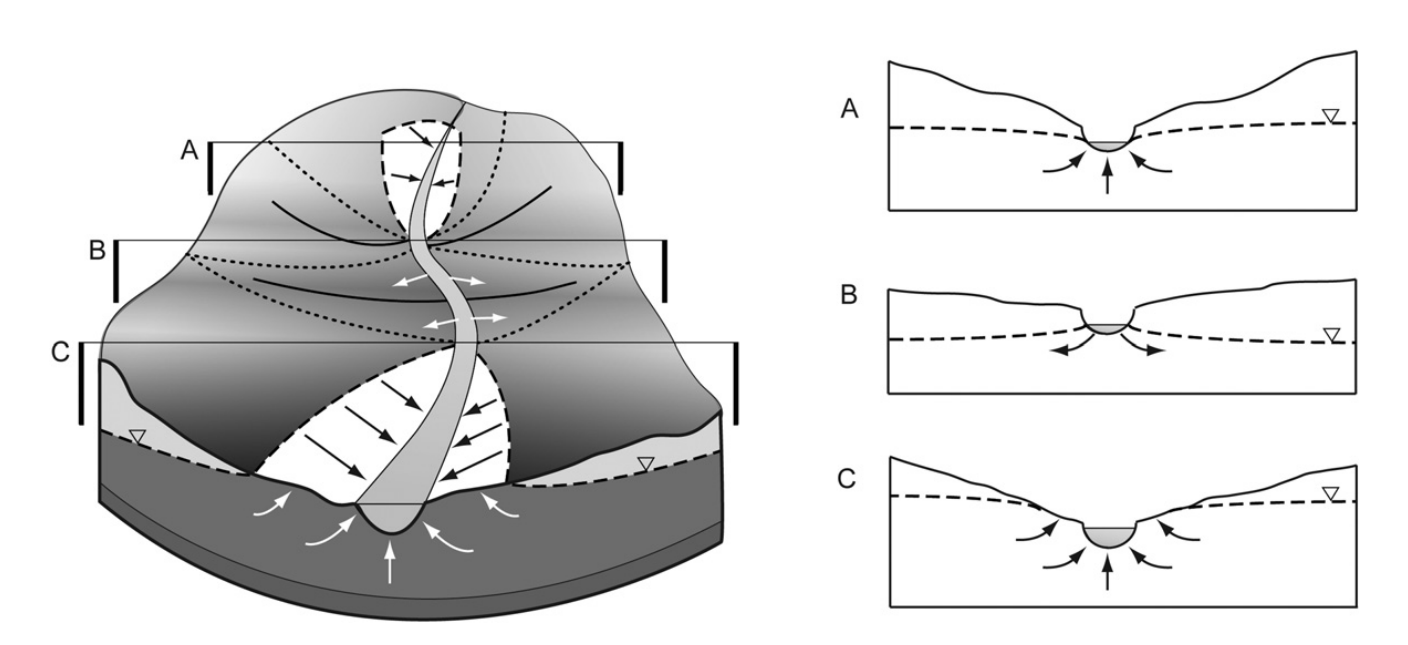
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – A hydraulic mixing-cell method to quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within spatially distributed fully integrated surface water–groundwater flow models
This research highlight co-authored by D. Partington, P. Brunner, C.T. Simmons, René Therrien, A.D. Werner, G.C. Dandy, and H.R. Maier, introduces a hydraulic mixing-cell (HMC) method to accurately quantify the groundwater component of streamflow within fully integrated surface–subsurface hydrologic models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to address long-standing challenges in decomposing streamflow generation mechanisms without relying on tracer transport simulations or simplifying assumptions about groundwater discharge.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM February 2026 (REVISION 2918)
The HydroGeoSphere February 2026 release is now available for download.

HydroGeoSphere Development 2025: The Year in Review - Aquanty Webinar
We’re pleased to share the recording of our webinar ‘HydroGeoSphere Development 2025: The Year in Review’. This session, presented by Dr. Killian Miller, Numerical Analysis Specialist at Aquanty, looks back at a year of major advancements to the HydroGeoSphere platform— highlighting new features, performance improvements, and key structural updates across the HGS ecosystem.
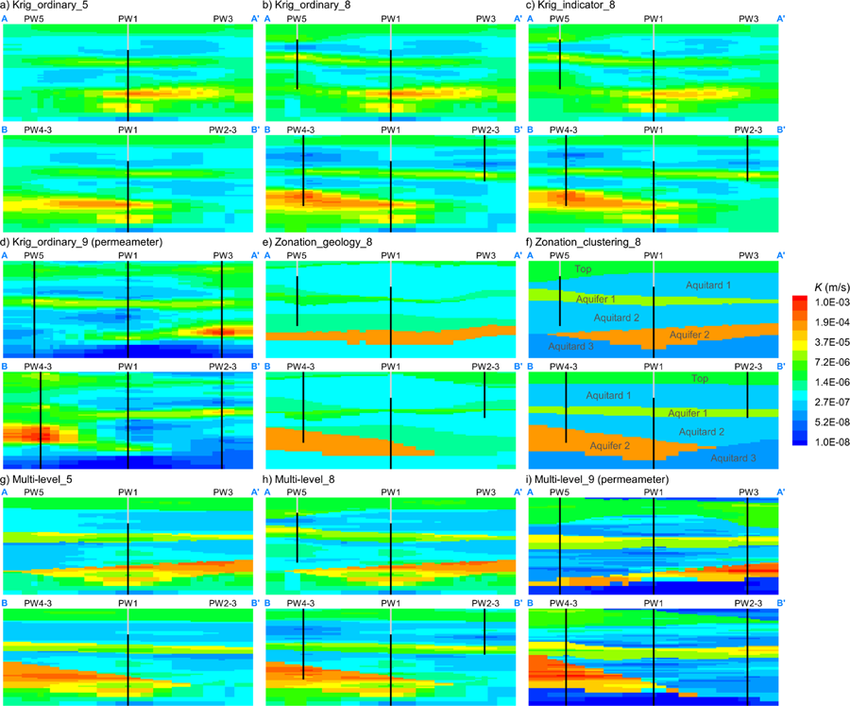
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Characterizing Spatial Heterogeneity of Hydraulic Conductivity Using Borehole NMR in a Complex Groundwater Flow System
This research highlight co-authored by Chenxi Wang, Colby M. Steelman, and Walter A. Illman, investigates how borehole nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) logging can be used to characterize subsurface heterogeneity and improve the representation of hydraulic conductivity in groundwater flow models. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to evaluate the predictive performance of NMR-derived hydraulic conductivity (K) models and assess how different spatial interpolation and upscaling approaches influence flow and drawdown predictions in a highly heterogeneous aquifer system.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM January 2026 (REVISION 2906)
The HydroGeoSphere January 2026 release is now available for download.

Introducing hgs2vtu for HGS model post-processing - Aquanty Webinar
We’re pleased to share the recording of our recent webinar introducing hgs2vtu.exe, the powerful new post-processing utility designed to modernize and streamline visualization of HydroGeoSphere (HGS) model outputs.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Natural and anthropogenic drivers of the water table dynamics in a riparian fen peatland
This publication, co-authored by Adrien Renaud, Claude Mügler, Véronique Durand, and Marc Pessel, which examines the natural and anthropogenic drivers of water table dynamics in a riparian fen peatland along the Essonne River in France. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) to couple surface and subsurface hydrology, providing new insights into how precipitation seasonality, vegetation activity, and river regulation influence peatland water levels.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM December 2025 (REVISION 2898)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2898 (December 2025) is now available for download.
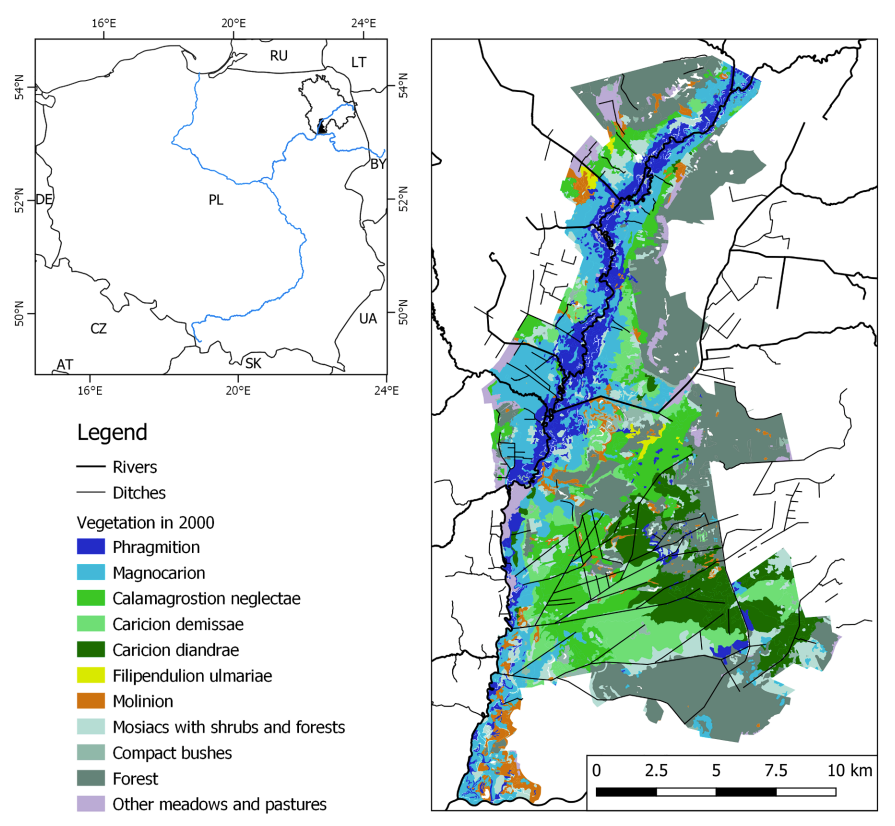
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Using water sources extent during inundation as a reliable predictor for vegetation zonation in a natural wetland floodplain
We’re pleased to highlight this publication, co-authored by Tomasz Berezowski and Martin Wassen, which investigates how the extent of water sources during inundation can be used as reliable predictors of vegetation zonation in wetland floodplains. This study leverages HydroGeoSphere (HGS) together with the Hydraulic Mixing-Cell (HMC) method to address long-standing challenges in modelling vegetation dynamics by explicitly accounting for the spatial distribution of different water sources during floods.
