

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Groundwater flow and age in topography-driven groundwater flow systems with geological barriers
The research examines how groundwater age and flow systems are influenced by topography and geological barriers, using numerical simulations to clarify the interaction between surface-driven flow and subsurface heterogeneity. Traditional models of topography-driven flow often assume homogeneous geologic conditions, which can obscure the role of stratigraphic variations in shaping groundwater movement and age distribution. This study offers a detailed exploration of how structural barriers— such as low-permeability formations— interrupt or redirect groundwater pathways and affect the spatial and temporal distribution of groundwater age.

Staff Research Highlight - Improving precision in regional scale numerical simulations of groundwater flow into underground openings
The study presents a novel numerical framework to improve the accuracy of regional-scale groundwater flow simulations into underground openings, such as tunnels and deep geological repositories. Traditionally, simulating groundwater inflows into engineered underground structures has involved significant simplifications, often treating tunnels as drain features or imposing boundary conditions that fail to fully capture the physical behavior of fluid flow around these voids. This research addresses those limitations by introducing a new numerical boundary condition to simulate groundwater flow into underground openings more accurately.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT - Is the Water Balance of Your Waste Rock Pile Reliable? A framework for Improving Assessment of Water Inputs and Outputs for a Typical Storage Facility
This research focuses on understanding the dynamics of topography-driven groundwater flow systems using fully-coupled surface–subsurface hydrologic modelling. This study addresses long-standing challenges in representing nested flow systems by simulating interactions between climate, topography, and groundwater without relying on potentially unrealistic, static boundary conditions.

Assessing the Sensitivity of Subsurface Mine-Dewatering Simulations to Surface Water Representation - Aquanty Webinar
Explore how surface water representation shapes subsurface mine-dewatering simulations in our latest webinar with Dr. Andrea Brookfield (University of Waterloo). This session highlights how climate change and surface water interactions can significantly influence dewatering strategies across mining operations.
Using HydroGeoSphere, the webinar compares conventional groundwater-only models with fully integrated surface–subsurface simulations under future climate scenarios. The results reveal important limitations of traditional approaches and show how integrated models provide more accurate insights for long-term mine water management.
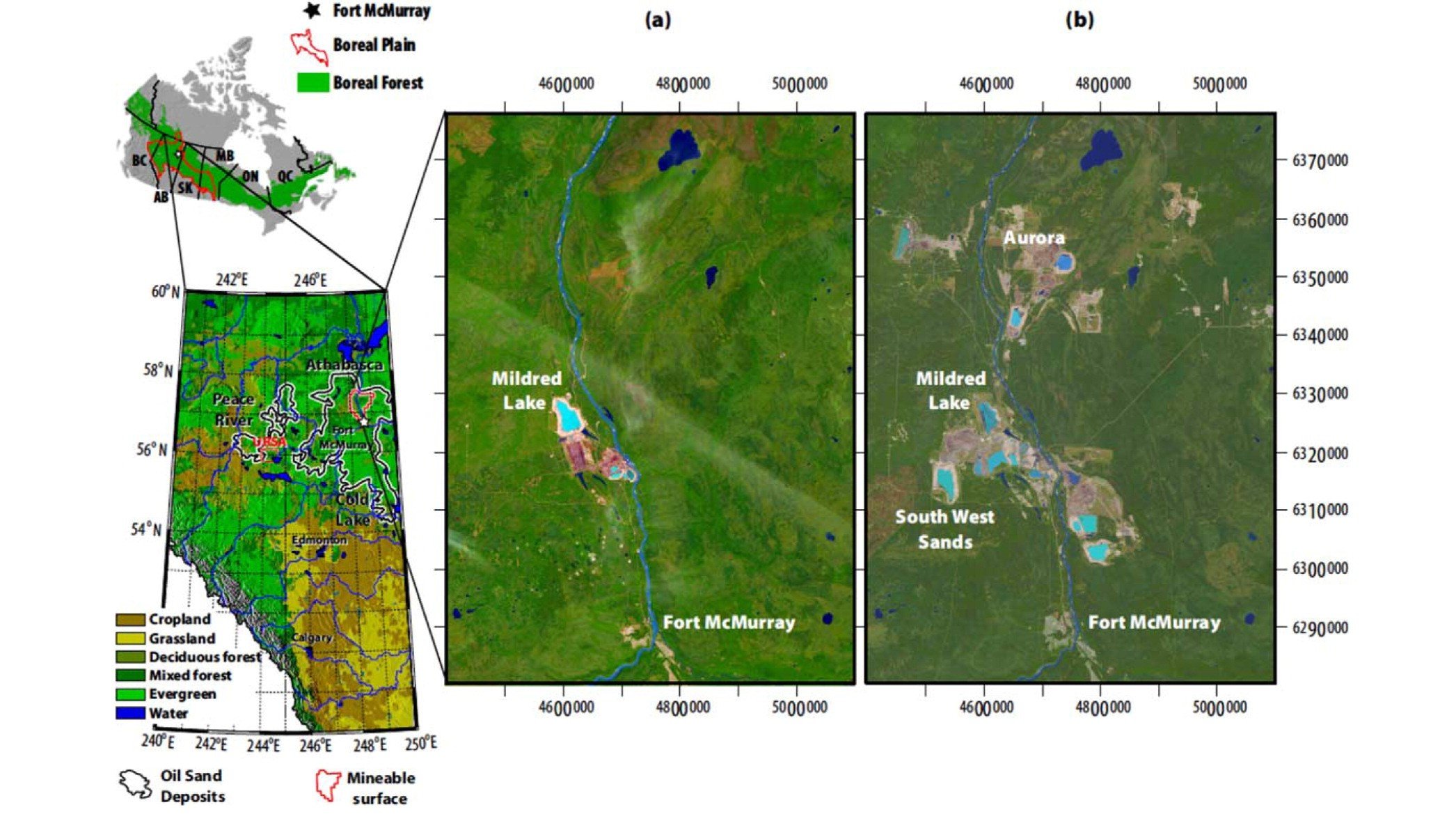
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Reclamation for aspen revegetation in the Athabasca oil sands: Understanding soil water dynamics
We’re pleased to highlight this publication which focuses on understanding soil water dynamics in reclaimed landscapes within the Athabasca oil sands region using unsaturated flow modeling. The study explores how different reclamation strategies affect soil water availability and water table fluxes— critical components for supporting aspen revegetation, a key species in boreal forest ecosystems.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Reactive transport modelling of acid mine drainage within discretely fractured porous media: Plume evolution from a surface source zone
This paper investigates the fate and transport of acid mine drainage (AMD) through fractured porous media using a discrete fracture network (DFN) modelling approach. This research addresses a critical environmental challenge in mining regions— predicting how acidic contaminants generated by sulphide mineral oxidation migrate through complex geological formations and interact with host rocks over time.

Staff Research Highlight - A dynamic meshing scheme for integrated hydrologic modeling to represent evolving landscapes
Aquanty is pleased to introduce a novel dynamic meshing scheme for integrated hydrologic modelling with HydroGeoSphere to better represent evolving landscapes. The approach addresses a major challenge in modelling human-altered environments, particularly in regions undergoing rapid changes such as open-pit mining sites, land reclamation zones, or urban developments. Traditional hydrologic models often rely on static mesh geometries, limiting their ability to capture changes in topography and subsurface structure over time. This research proposes a more flexible, adaptive framework capable of simulating surface and subsurface hydrologic responses to complex engineering activities.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Numerical analysis of thermal response tests with groundwater flow and heat transfer model
This research, co-authored by J. Raymond, L. Gosselin, R. Lefebvre, and Aquanty’s René Therrien, explores how thermal response tests (TRTs) can be enhanced by employing HydroGeoSphere (HGS), our advanced modelling platform, to simulate coupled groundwater flow and heat transfer processes under complex geological settings. The study investigates the limitations of traditional line-source models, particularly in heterogeneous subsurface conditions, and introduces a numerical modelling approach to improve the accuracy of TRT analyses.
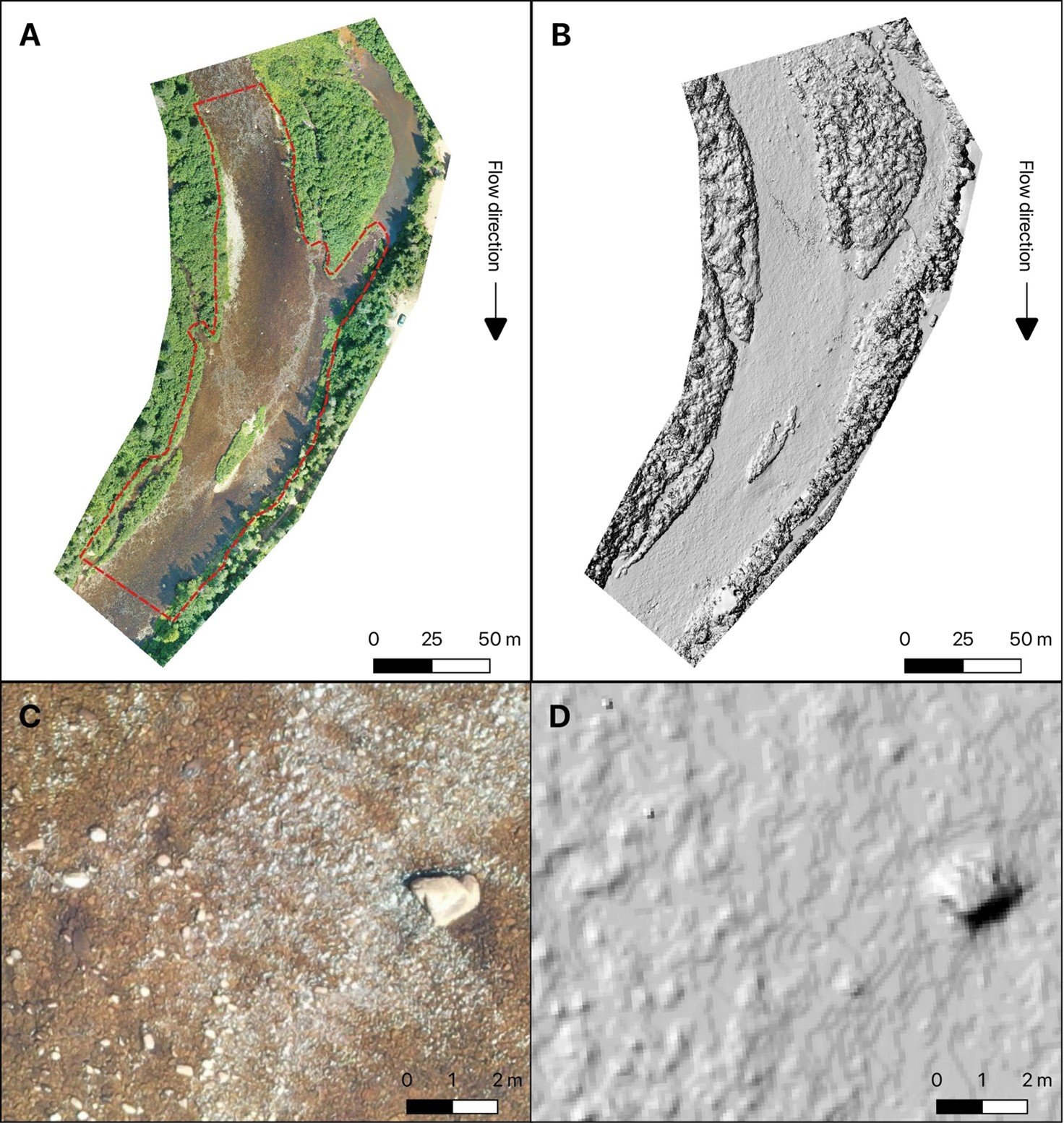
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – The HypoSalar project: Integrating hyporheic exchange fluxes into Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) spawning habitat models
In this research highlight ultra-fine resolution HydroGeoSphere models are used to simulate hyporheic exchange fluxes in river reaches used by Atlantic salmon for spawning. The HypoSalar project is contributing to demonstrate that the capabilities of HydroGeoSphere are not exclusively related to the field of hydrogeology, but can be used for both fluvial geomorphology and ecological studies due to HydroGeoSphere's flexibility and superior modeling approach.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Analyzing variation of the water table level with three-dimensional numerical simulations to assess reclamation techniques for an acidic tailings impoundment
As an extension of the last HGS research highlight titled ‘Improving control of contamination from waste rock piles’, this next research highlight within this series looks at a study conducted by the same researchers and explores the effects of thin cover deposition on managing water table levels in acidic tailings impoundments, while utilizing HydroGeoSphere (HGS) for in-depth simulations.
