

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Exploring the reliability of ²²²Rn as a tracer of groundwater age in alluvial aquifers: Insights from the explicit simulation of variable ²²²Rn production
We’re pleased to highlight this publication which investigates the reliability of using radon-222 (²²²Rn) as a tracer for groundwater age in alluvial aquifers. Accurate estimations of groundwater residence time (GRT)—the time since water infiltrated from the surface—are critical for effective water resource management, especially in systems that rely on bank filtration near rivers for drinking water supply. While ²²²Rn has long been employed as a natural tracer due to its radioactive decay properties and elevated concentrations in groundwater, most traditional models assume spatially uniform ²²²Rn production and purely advective flow— assumptions that rarely hold in real-world aquifers.

Staff Research Highlight - Application of Different Weighting Schemes and Stochastic Simulations to Parameterization Processes Considering Observation Error
In this paper co-authored by Aquanty personnel, researchers explore how different weighting schemes and stochastic simulations can enhance the accuracy of parameter estimation processes, ultimately reducing uncertainty in climate change impact assessments.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM July 2025 (REVISION 2853)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2853 (July 2025) is now available for download.
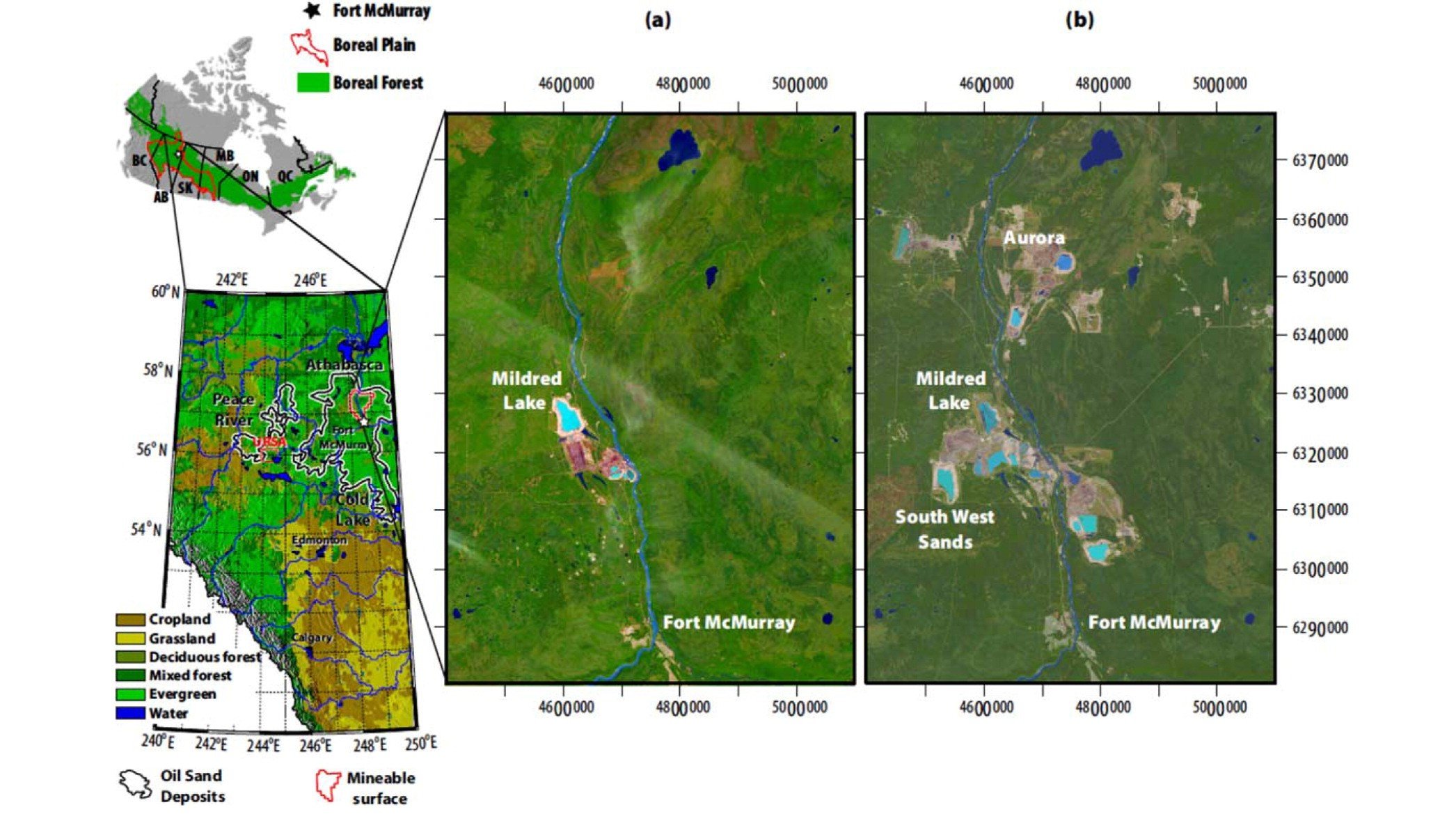
HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Reclamation for aspen revegetation in the Athabasca oil sands: Understanding soil water dynamics
We’re pleased to highlight this publication which focuses on understanding soil water dynamics in reclaimed landscapes within the Athabasca oil sands region using unsaturated flow modeling. The study explores how different reclamation strategies affect soil water availability and water table fluxes— critical components for supporting aspen revegetation, a key species in boreal forest ecosystems.

HGS RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT – Reactive transport modelling of acid mine drainage within discretely fractured porous media: Plume evolution from a surface source zone
This paper investigates the fate and transport of acid mine drainage (AMD) through fractured porous media using a discrete fracture network (DFN) modelling approach. This research addresses a critical environmental challenge in mining regions— predicting how acidic contaminants generated by sulphide mineral oxidation migrate through complex geological formations and interact with host rocks over time.

HydroGeoSphere Canada Day Software Sale Announcement
To mark Canada Day and celebrate the impact of Canadian-made technology in the field of hydrology, we’re offering exclusive discounts throughout the month of July for all new commercial users of HydroGeoSphere!

Staff Research Highlight - A Continuous Differentiable Formulation for Seepage Face Boundary Conditions in Dynamic Groundwater Systems
This research by Aquanty staff introduces a continuously differentiable formulation for seepage face boundary conditions in dynamic groundwater systems. Traditional approaches often model seepage faces with abrupt boundary transitions, leading to numerical instabilities, convergence issues, and computational inefficiencies in transient groundwater simulations. This research presents a novel approach that ensures smooth transitions between saturated and unsaturated zones, improving the stability and accuracy of numerical groundwater models.

NEW version of HGS PREMIUM June 2025 (REVISION 2845)
The HydroGeoSphere Revision 2845 (June 2025) is now available for download.
